What is Oxidation?
Oxidation is a chemical reaction in which electrons are LOST by atoms, ions or molecules. Reduction is the GAIN of electrons. Regardless of the name similarity, oxidation reactions need not actually involve oxygen atoms or molecules.
Oxidation, for non-chemists and those who have forgotten high school chemistry, is commonly just burning or rusting. If done instantaneously, it is an explosion. If done rapidly, it is burning. If done slowly, it is corrosion. When acting at a molecular level, it is just plain oxidation, or part of the oxidation-reduction process. It can occur in gaseous or solid states as well as in liquids.
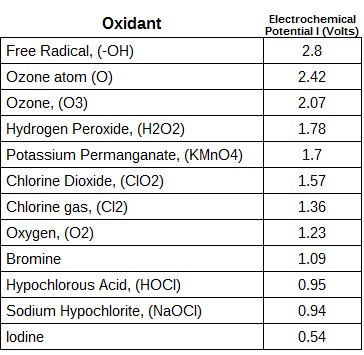
Ozone has one of the highest oxidation potentials, lower only than flruorine atom, oxygen atom, and hydroxyl radical. Some of the reactions of ozone create the oxygen atom and hydroxyl radical to create an even higher oxidation potential than ozone alone.
Because of the high oxidation potetnail the oxygen molecule has a high capacity to react with many compounds not easiy oxidized by other chemicals. This potential is especially important reactions with some inorganic species such as FE+2 and I-. However, in many cases there is no explicit electron transfer, but rather an oxygen transfer from the ozone molecule to the other compound.
Example of ion exchange oxidation of ozone and iron:
Fe+2 + O3 = FE+3 + O3-
Example of oxygen atom exchange oxidation of ozone and iron:
2Fe2+ + O3 + H2 O → 2Fe3+ + O2 + 2OH-
Both reactions can occur with organic and inorganic compounds. This is just one simple example of ozone oxication reactions.

Right here is the right blog for anybody
who wishes to find out about this topic. You understand so much its almost hard to argue with you
(not that I really will need to…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic that has been written about for decades.
Great stuff, just excellent!
Oxidizing agent is reduced in a reaction. So it should be compared with reduction potentials. A good oxidising agent should have high reduction potential. In the table it is given that oxidising agents have high oxidation potential. Plz help to clear my doubt.