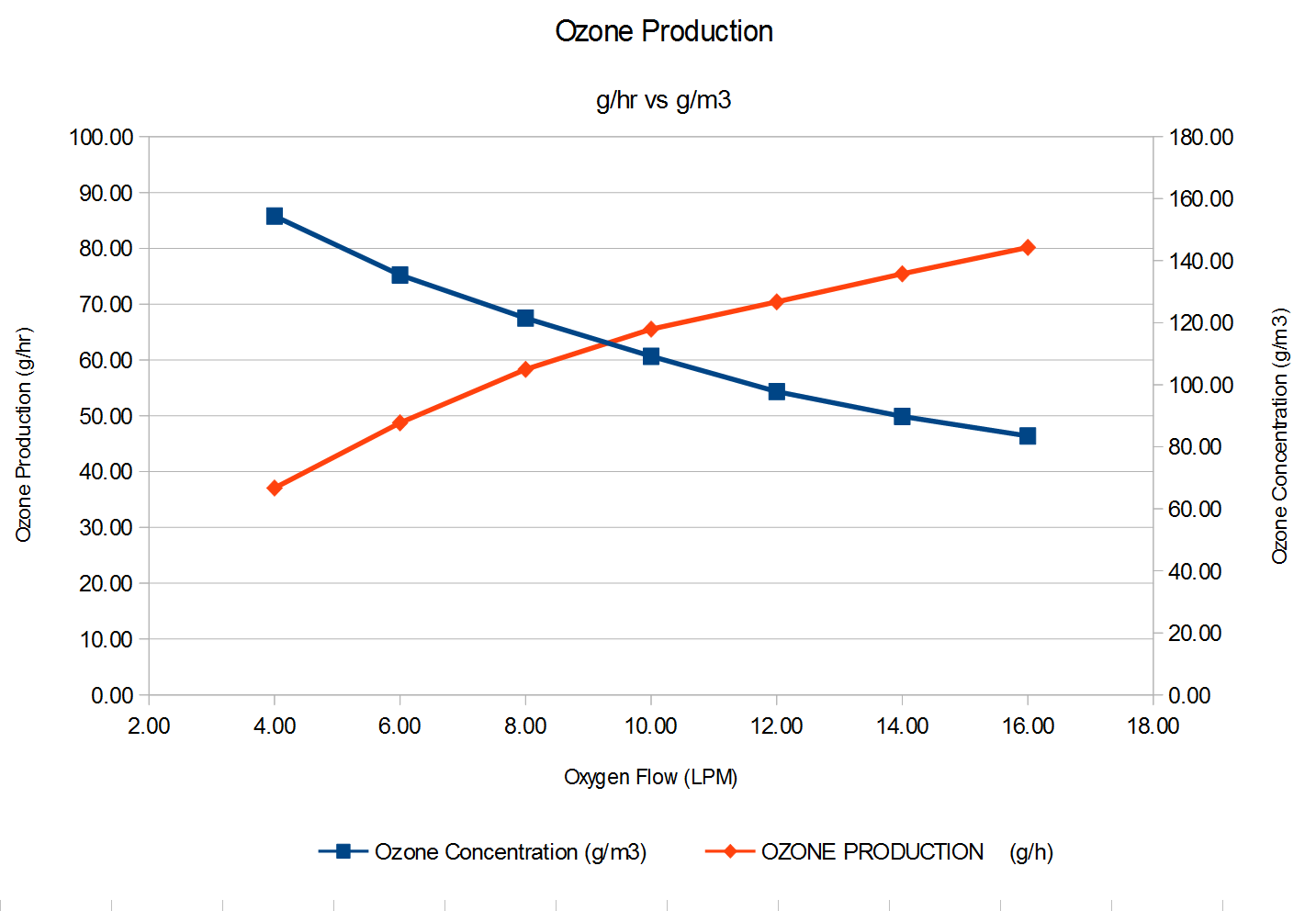
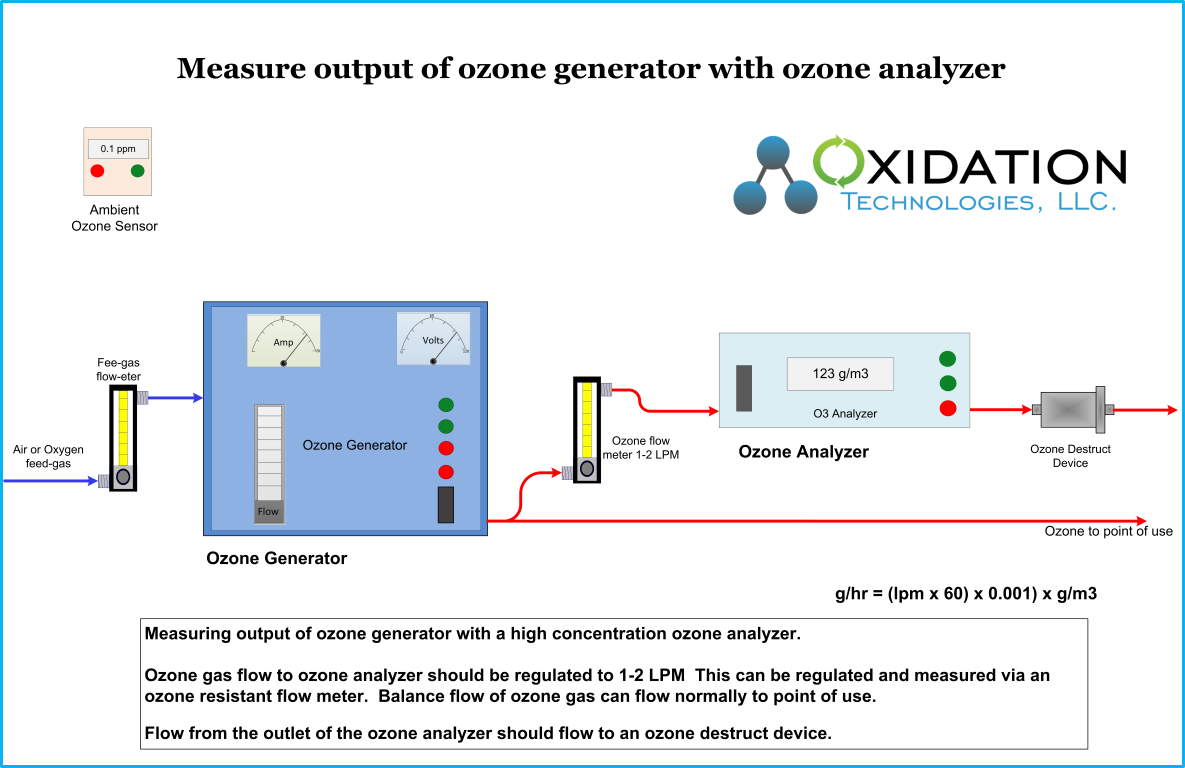
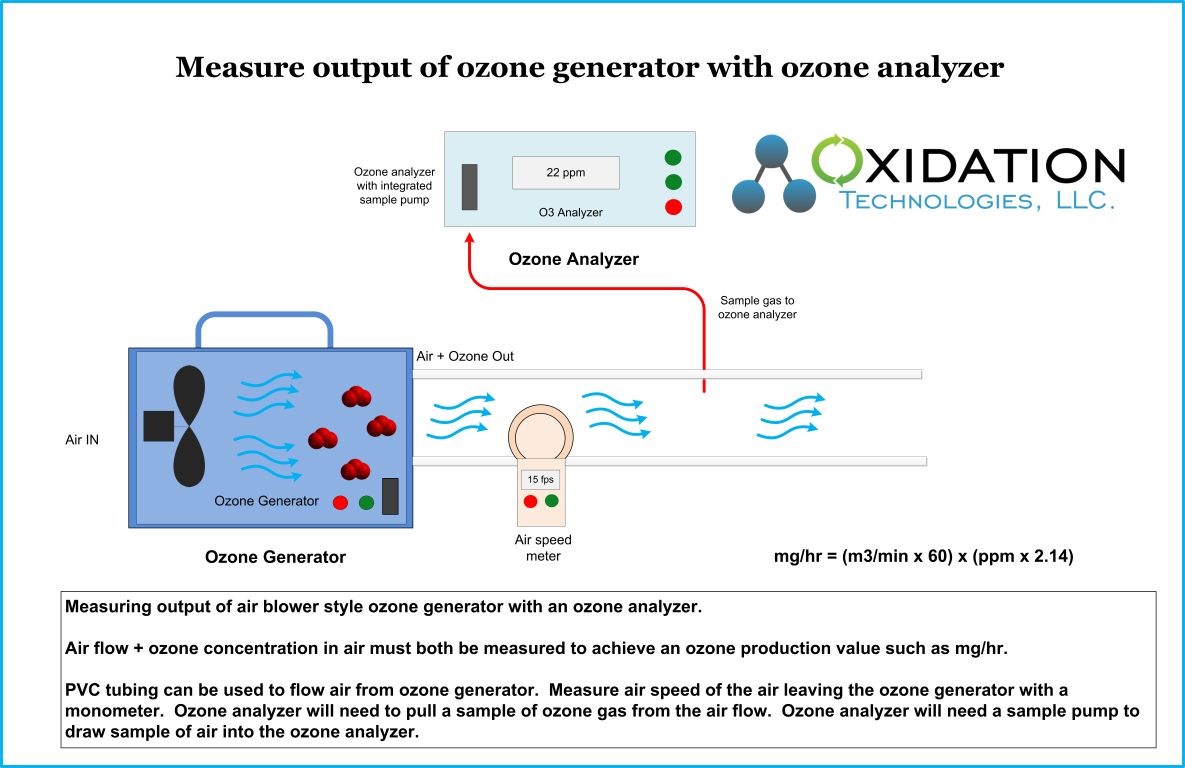
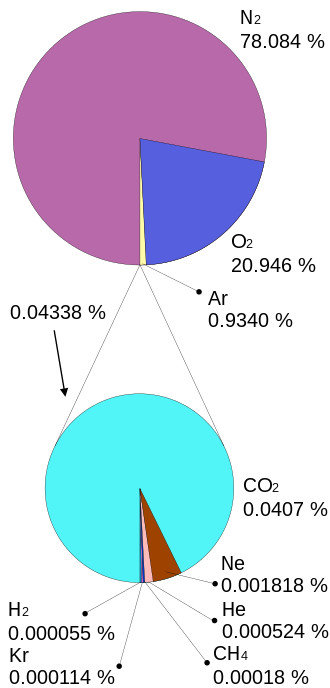
Ozone Info
Ozone is a gas that is found in nature (the ozone layer) but can also be produced for commercial and industrial applications. The uses of ozone are many, and growing every day. This is a beginning introduction to ozone and will provide a basic understanding of what ozone is, how it is used, and the application of commercial ozone use in our world today.
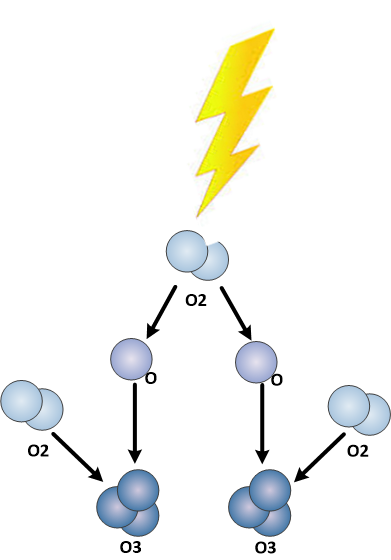
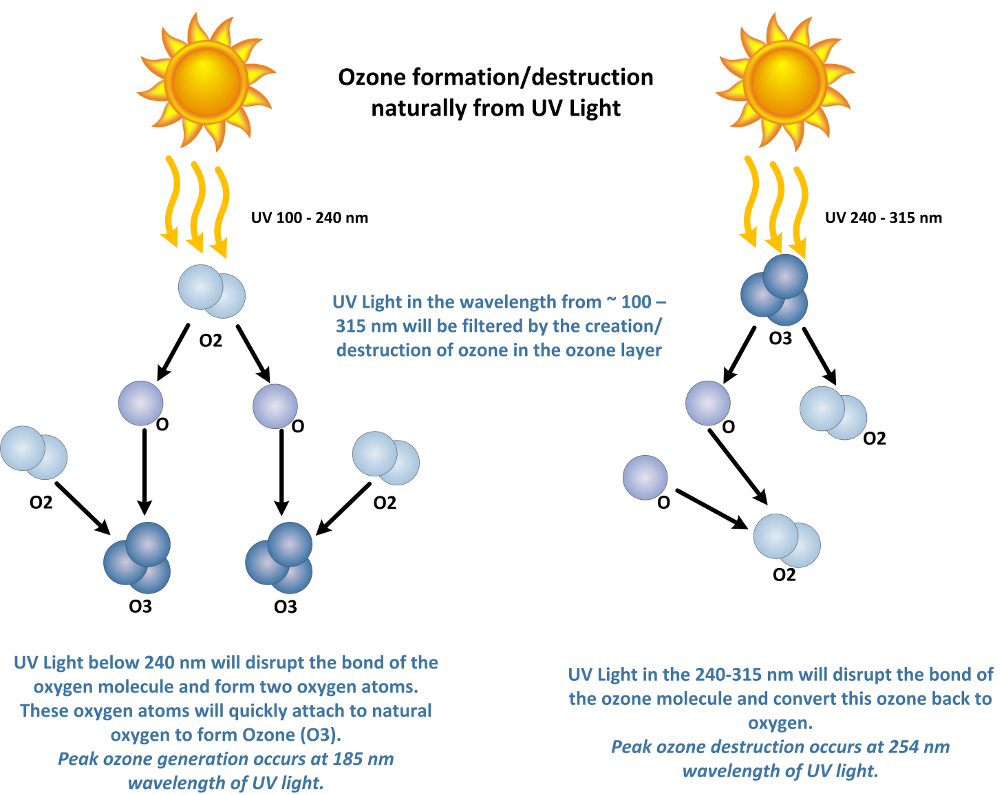
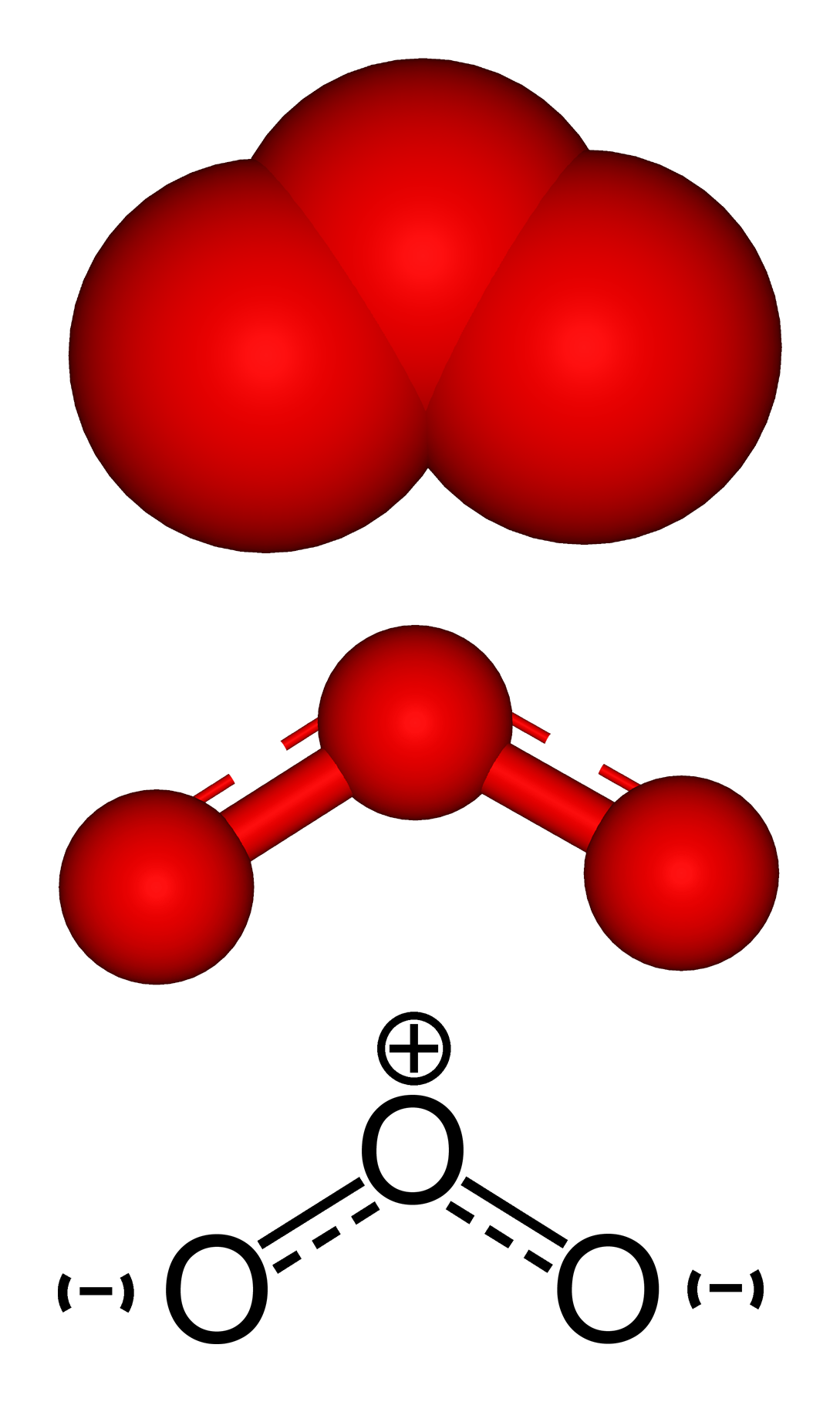
Ozone is a triatomic form of oxygen, three oxygen atoms together to form one molecule.
What is Ozone?
The oxygen atom is unstable in the atomic form. Oxygen is stable in the diatomic form as O2. The air we breathe today is made up of about 21% oxygen, this makes oxygen one of the most common molecules found in nature today.
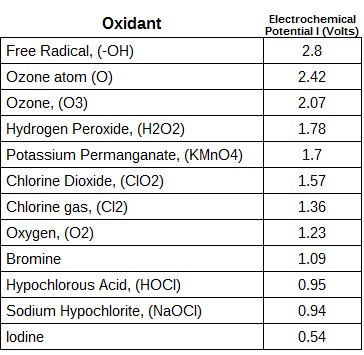
Ozone is a triatomic form of oxygen, meaning that the molecule, ozone, is made up of 3 oxygen atoms. Unlike oxygen, ozone is a visible gas with a light blue color at very high concentrations. At low concentrations ozone is colorless. Ozone also has a distinct odor that is noticeable at very low levels and may be associated with a “clean” smell, at higher levels ozone has a very pungent odor. Ozone is an unstable gas that readily decomposes to oxygen naturally. Ozone is also a highly reactive gas that acts as a very strong chemical oxidant.
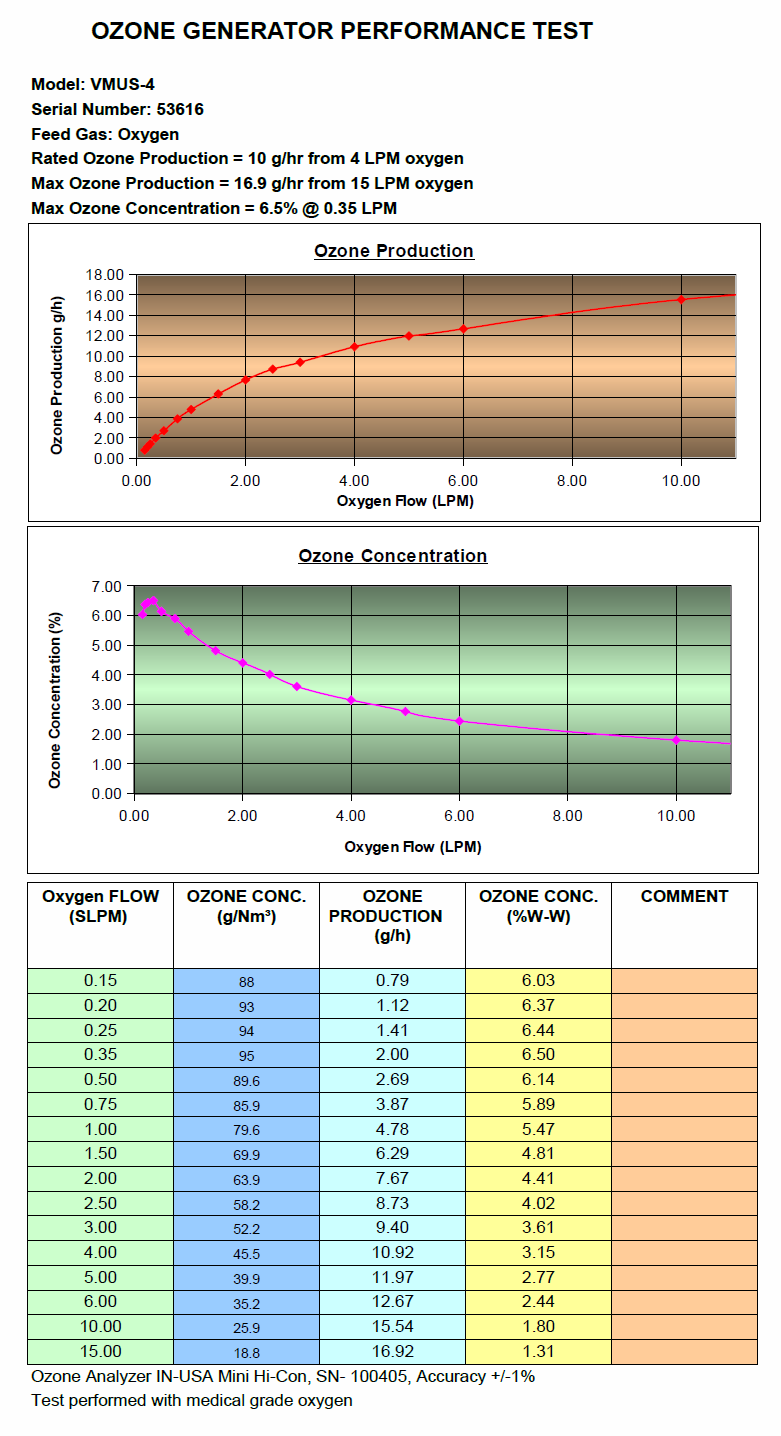
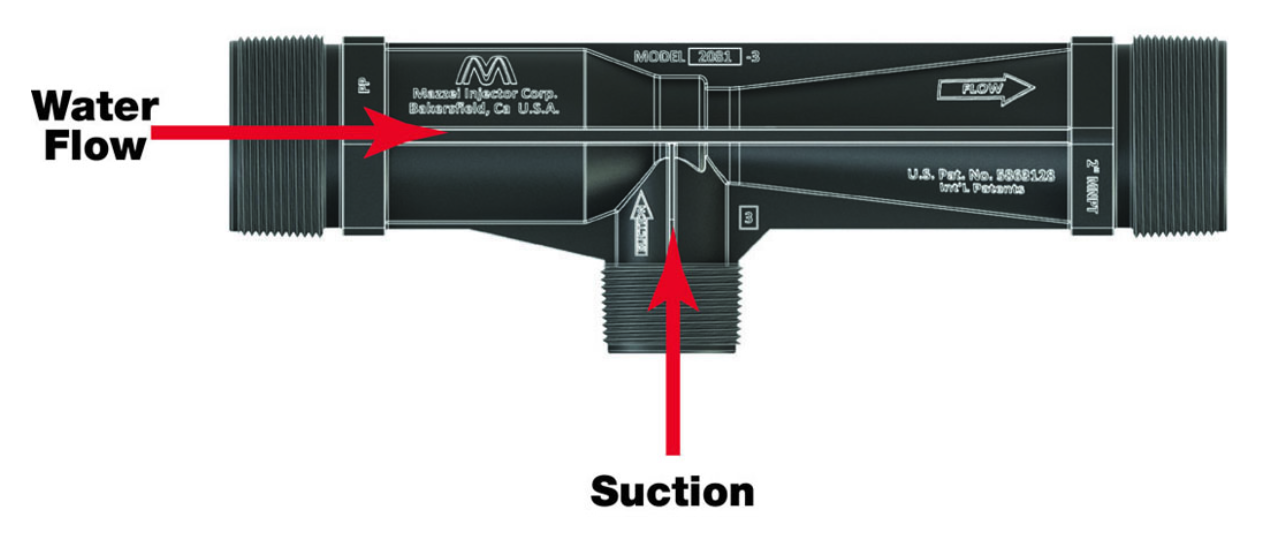
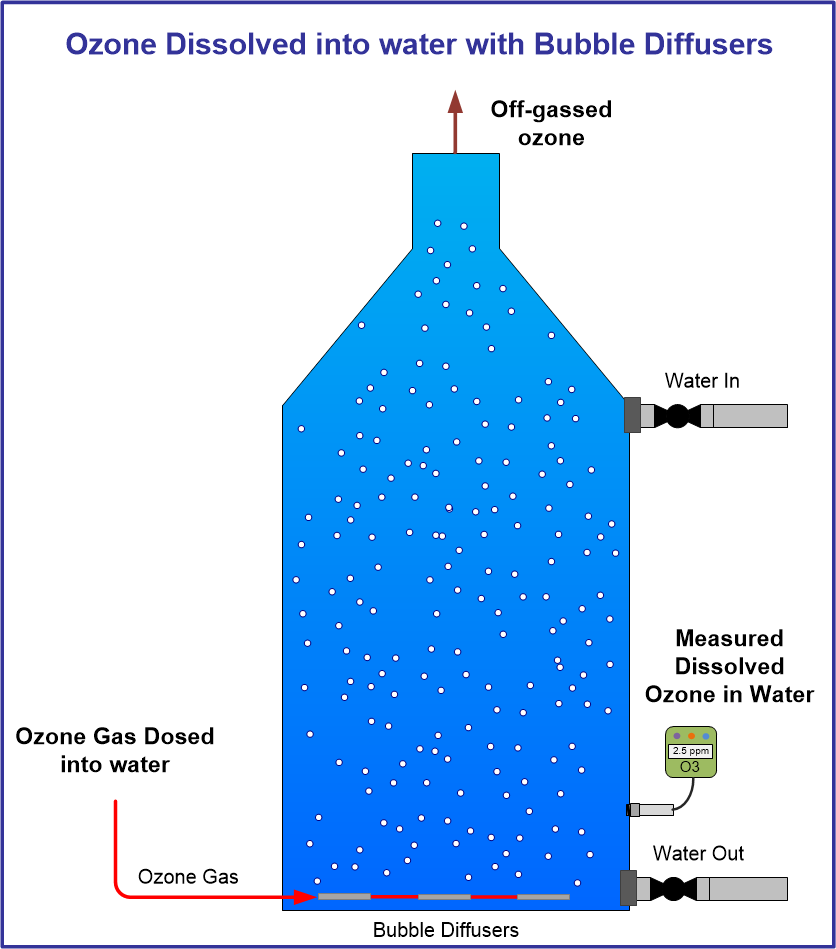
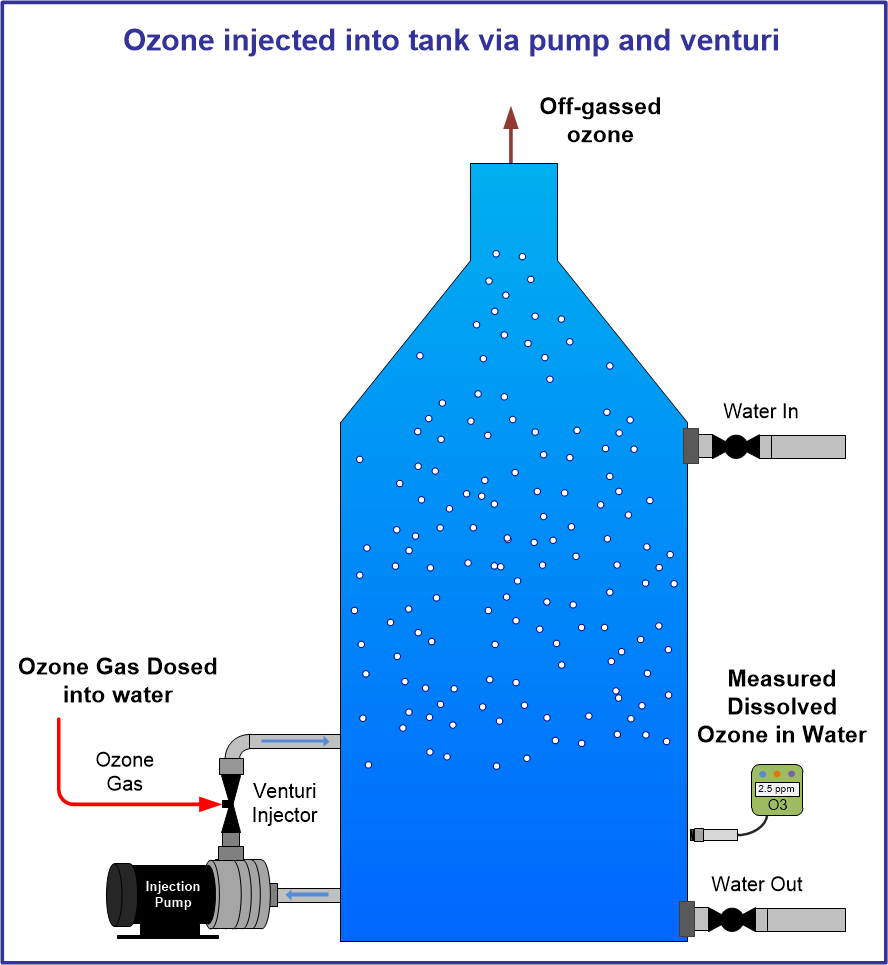
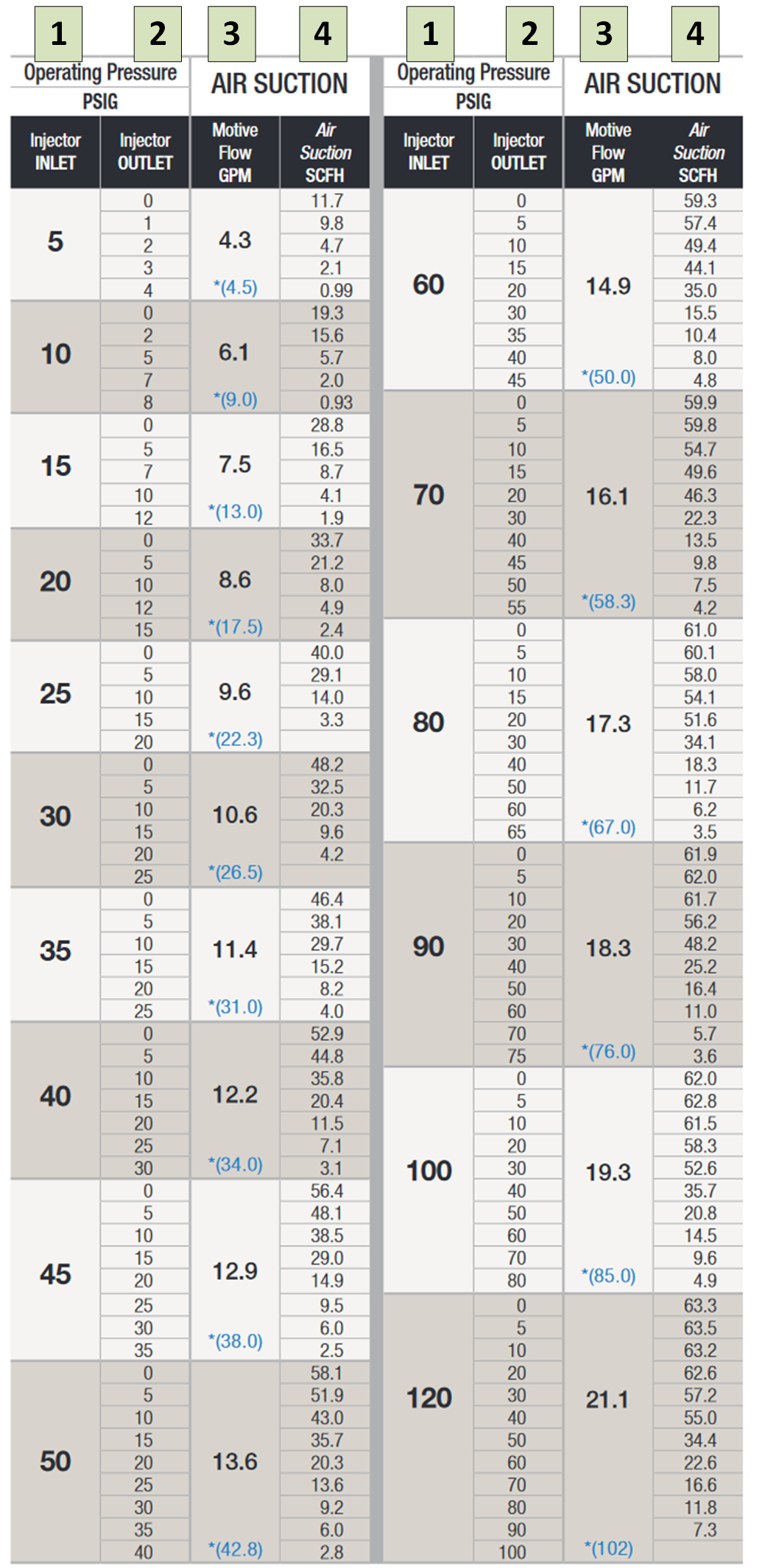
Click Images in table below for specific ozone information:
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Ozone Regulations in Food Processing
|
|
|
|
|
|
|