Agri-Food Processing
Ozone was given GRAS approval by the FDA and the USDA in 2001. This GRAS approval allows the use of ozone for direct contact with food as an antimicrobial intervention. Ozone use can provide safer food that will have a longer shelf-life due to lower bacteria levels. Ozone can be used on many food products.
How it works:
Ozone as an oxidant is useful in the inactivation of all pathogens yet reverts to oxygen after oxidation leaving no undesirable by-products on food products. Ozone is effective at eliminating all pathogenic bacteria, along with viruses and mold. Ozone is effective against bacteria at very low levels as the ozone reaction with bacteria causes lysis of the cell wall causing the cell wall to rupture through the oxidation process. However, chlorine requires the diffusion of HOCL through the cell membrane. There are no "ozone resistant" bacteria strains. Inactivation rates of bacteria due to ozone will be dependent upon ozone concentrations, time, temperature and humidity (in gas phase).
Ozone can be used in the gas and aqueous phase for effective inaction of food-borne pathogens.
Aqueous Ozone:
The most common method of using ozone for pathogen reduction is dissolving ozone into water. Aqueous ozone is very stable, safe, and easy to manage. Typically ozone is dissolved into water using an ozone injection system and then sprayed onto the surface requiring disinfection. This surface may be a hard equipment surface, or the surface of a food product.
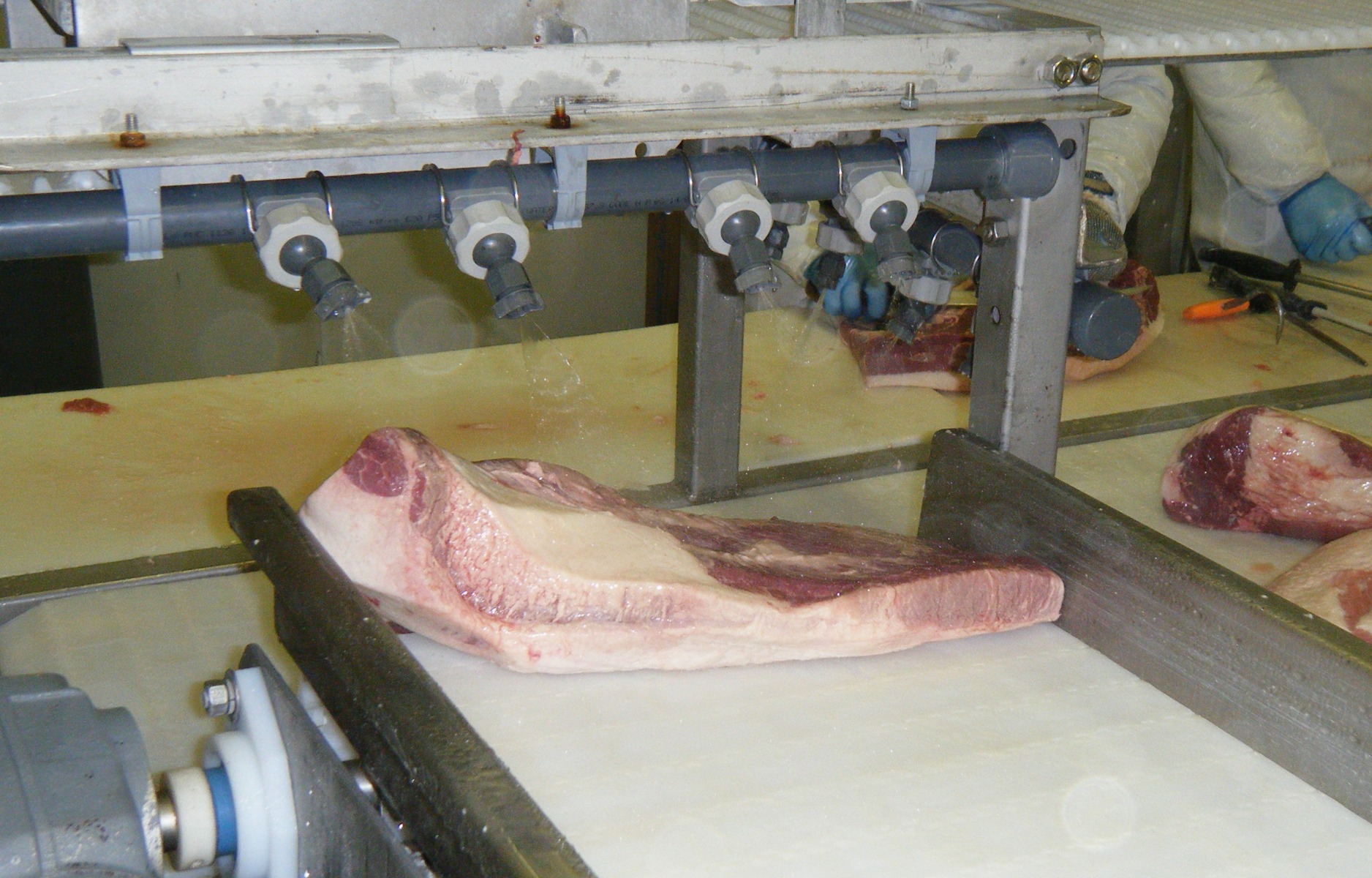

Ozone levels dissolved into water of only 2.0 ppm or above are commonly used for bacteria inactivation. Only a few seconds of contact time of the aqueous ozone with the pathogen is necessary for inactivation. While greater ozone levels in water can be used with no adverse effects to the food, there is minimal benefit to initial sanitation using higher levels of ozone
See the chart below for details.
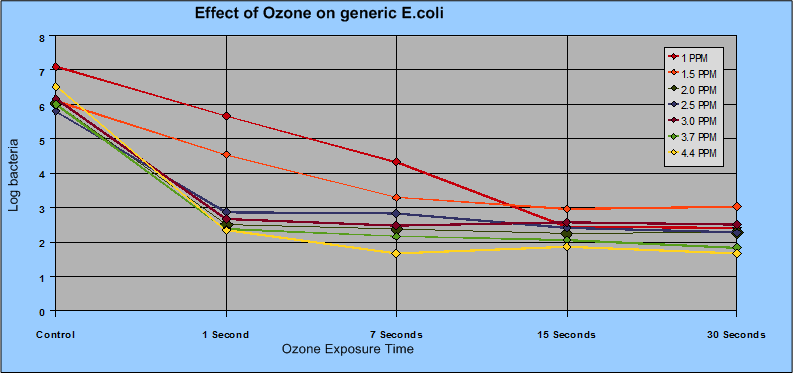
Using this data a determination of spray nozzles, spray bars, or even conveyers can be established. It is clearly shown that 2.0 ppm of aqueous ozone is very effective in only a short period of time, while higher ozone levels show only marginal improvement.
It is important to note that ozone reverts to oxygen quickly. Therefore tanks of ozone water to dip food products into is normally not effective as the water will lose the ozone dissolved in water quickly. It is normally best to spray adequate levels of water on food products with sufficient dissolved ozone levels in this water.
Gaseous Ozone:
The use of gaseous ozone for the elimination of pathogens is also viable. The application of gaseous ozone is dependent upon the temperature, humidity, contact time, and ozone levels. Research has been conducted to determine that gaseous ozone will reduce and inactivate pathogens. However, this application normally requires closer adherence to specific temperatures and humidity in the room as the reaction rate of ozone gas will vary based on these factors.

Ozone GRAS Approval:
Ozone was granted GRAS (Generally Regarded as Safe) by the USDA and FDA due to a petition filed by the EPRI (Energy Partners Research Institute) in an effort to gain more widespread use of ozone in food processing as an effort to reduce energy consumption. Both the original petition and the final handbook assembled by the EPRI are available in the links below. Additional information on ozone regulations can be found HERE.
Due to GRAS approval granted for the use of ozone the implementation of ozone is allowable for all food applications in the USA with minimal additional regulation.
Ozone in Organic Food Production:
Ozone is allowed for use in the organic production of food products. The National Organic Program (NOP) has allowed for the use of ozone to varying degrees in various applications. For more information on the use of ozone in organic food production follow this link.
Potential Water Savings:
Ozone has been implemented in various applications to lower water consumption or waste along with reclaiming water for re-use in a food plant.
Closed-loop water systems can benefit from ozone use as ozone will oxidize organics in water while leaving no or minimal by-products when compared to other chemical options. By keeping water disinfected while maintaining clearer, cleaner, odor free, and chemical by-product free water system change-outs can be minimized saving water and saving processing time.
Ozone can be used to reclaim water from processes by offering disinfection, color removal, and odor removal from that water for use in secondary applications within the plant.
When used in CIP, or surface sanitation applications ozone can be used as a final sanitizer and rinsing step in one. As ozone reverts to oxgen there is no need for a secondary rinse step in various applications.
Benefits of Food Processing with Ozone:
-Bacteria reduction during processing will also extend shelf life
-Greater elimination of bacteria is realized with ozone
-Ozone was given GRAS approval by both the FDA and the USDA in 2001
-Fewer disinfection by-products will be created with the use of ozone, ozone reverts to oxygen
-Water savings may provide system pay-back
-Less chemicals = better flavor
-Lower chemical costs, overall lower costs
-Less chemicals in the environment ensures improved human safety
Ozone Food Processing Applications:
- E.coli o157:H7 Reduction with Ozone
- Listeria Inactivation with Ozone
- Red Meat Processing ozone ozone
- Surface Sanitation
- Seafood Processing
- Various Berries processing ozone ozone
This list is not comprehensive but links to various pages on our website with application specific information. Should you have questions about your unique application, contact our office, we would be glad to help.
Additional Links:
Ozone Regulations in Food Processing
Ozone regulations in Organic food production
Resolution Concerning the Use of Ozone in Food Processing from original EPRI documents
Original EPRI Direct Food Additive Petition used to gain GRAS approval for ozone
Book - Ozone in Food Processing
View the Questionnaire for Meat Processing Plant so we can help design your Ozone System