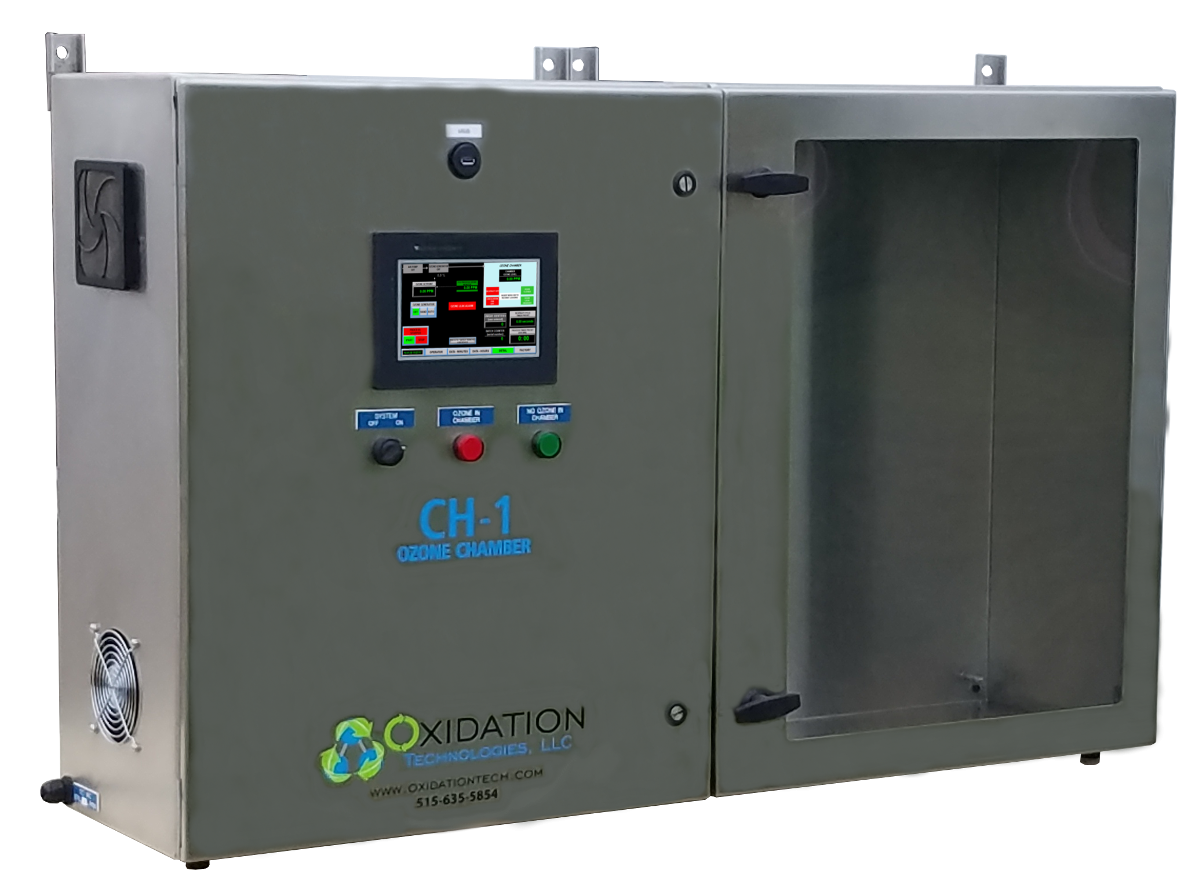
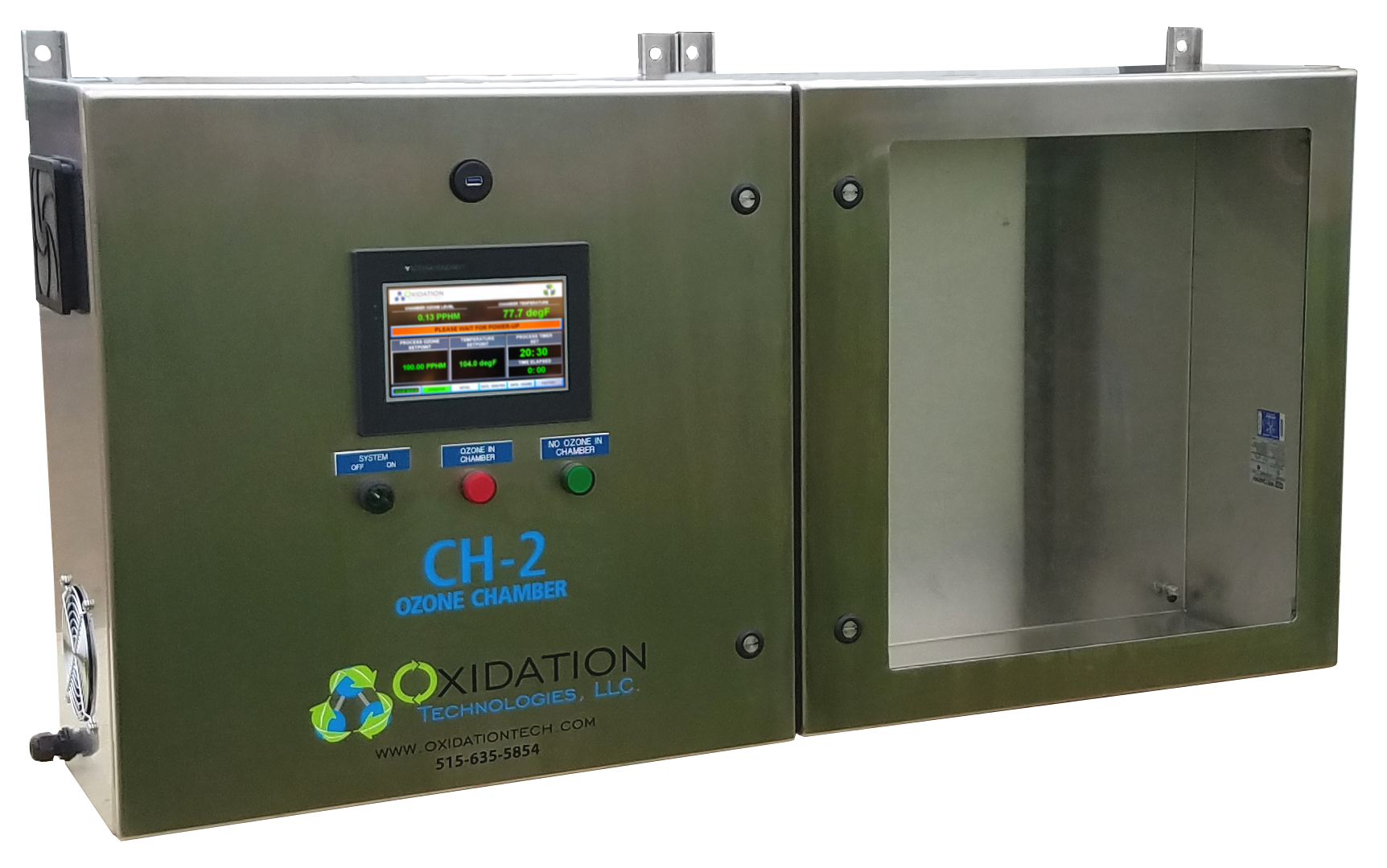
Ozone Exposure Testing
Oxidation Technologies provides ozone exposure testing services for many applications.
What is Ozone Exposure Testing?
Ozone Exposure Testing is a method used to determine the effect of a material exposed to ozone gas. This is accomplished using an Ozone Chamber with precise instrumentation and controls to create this environment. This test method can be used to estimate the life span of the material under normal conditions. This is called Accelerated Age Testing.
Other applications include:
Quality Assurance Testing
Research & Development
Odor removal
Scientific Research
Ozone Exposure Testing:
We have the tools and expertise to perform the ozone exposure portion of the test.
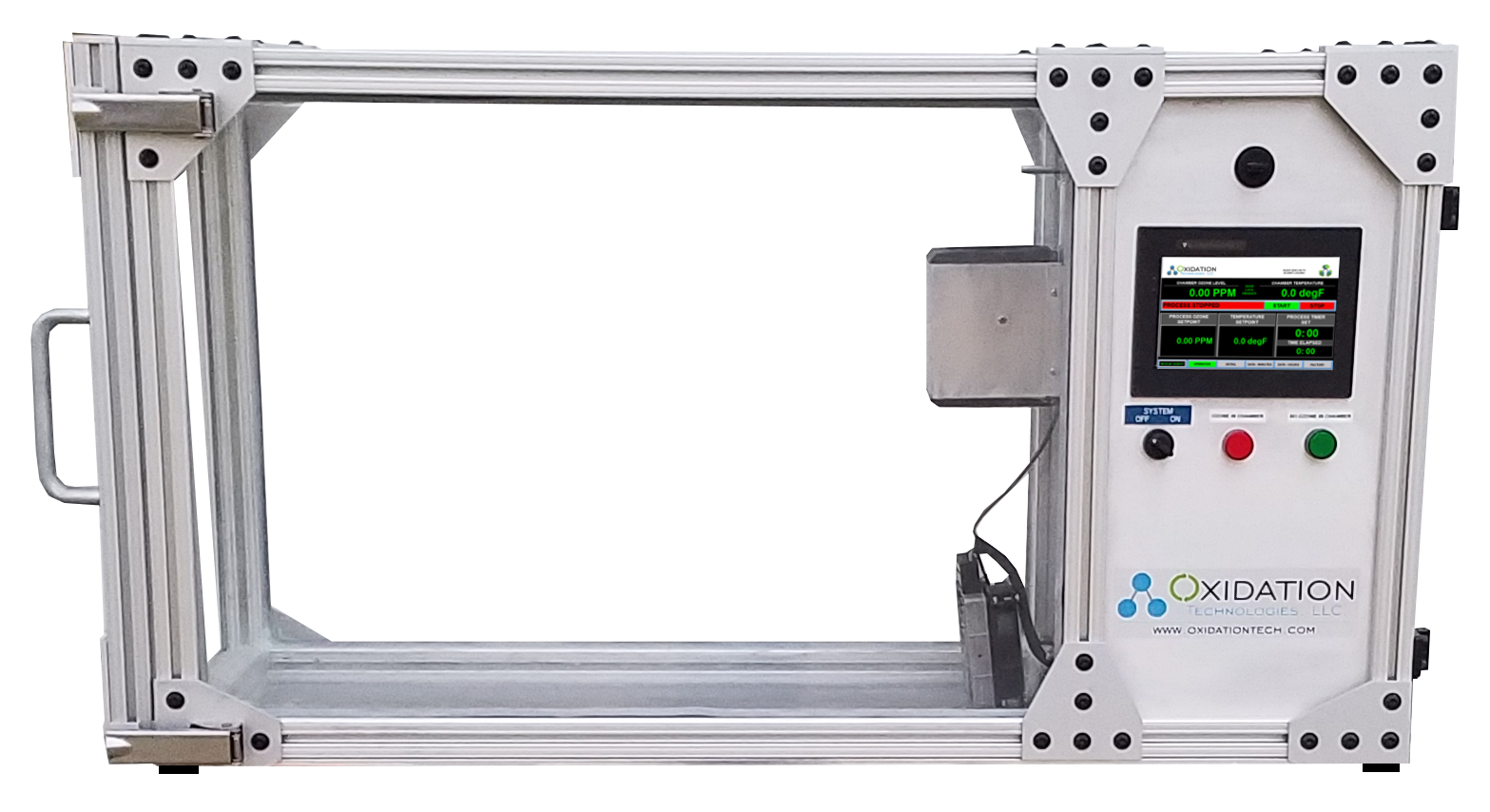
Oxidation Tech uses a calibration chamber with a dual beam ThermoFichsher Ozone Analyzer to create and measure ozone levels. This chamber is used for all in-house ozone sensor calibrations as well as Ozone Exposure Testing. We can run these exposure tests from 0-1000 PPM and up to 105 Degrees Fahrenheit.
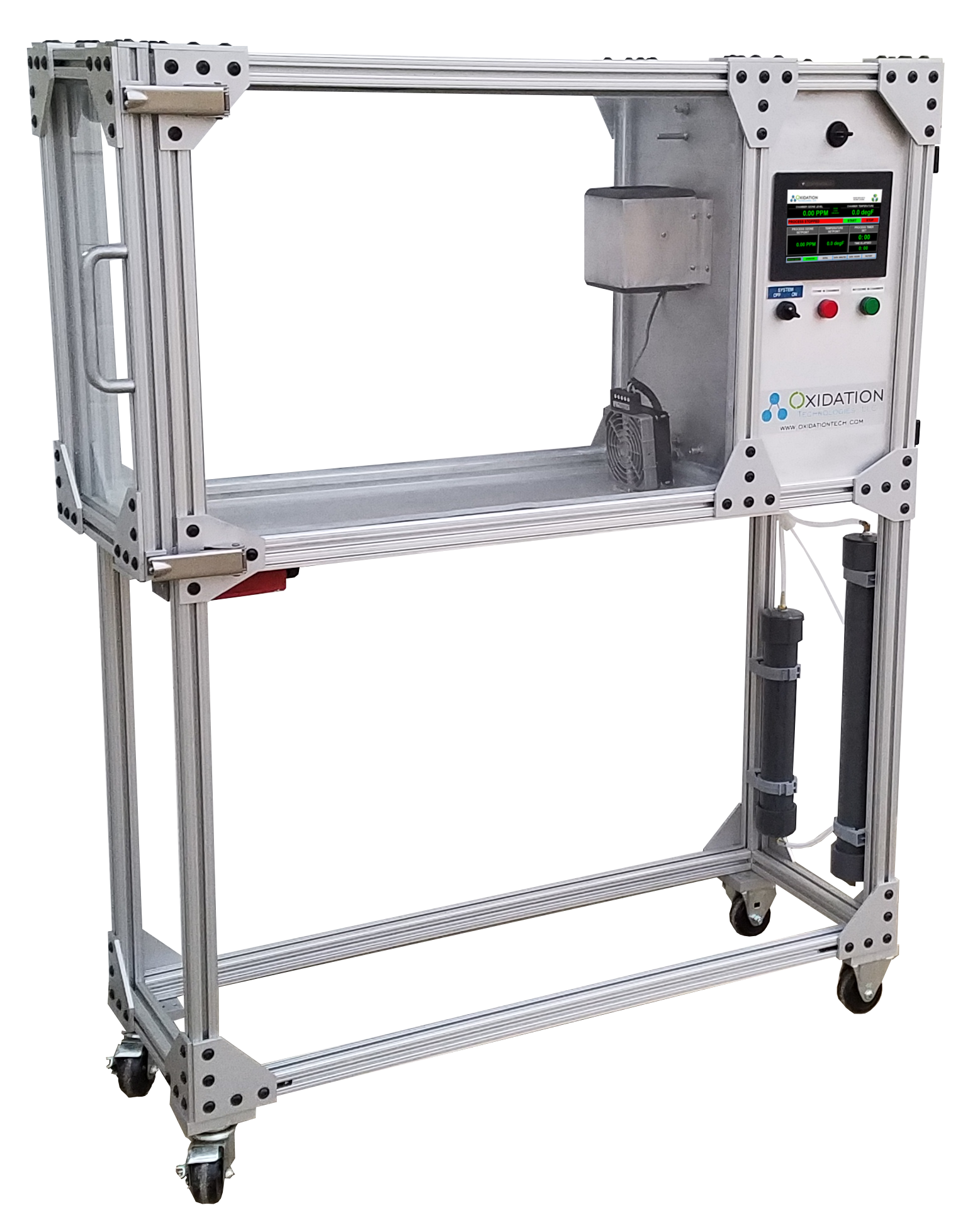

We can perform the exposure testing from hours to weeks if needed. All exposure testing includes a graph and raw data of ozone, temperature, and humidity levels.
Example of one of our ozone chambers in use:
JIS K6259 standards
ISO 1431
MIL-STD-202G
MIL-STD-1344
SAE J1455
SAE J517
SAE J1401
ASTM D1149-07
ASTM D1149-99
ASTM D1171
ASTM D3395
ASTM D4575
ASTM D518
ASTM D380
FMVSS 106
EIA-364-14
TP-14B
Ozone in water testing:
We can also offer ozone testing in water. Materials can be placed in water containing ozone at a specified ozone level and temperature for any period of time necessary. We have exposed materials to water in a bath, or pumped water containing ozone through parts if necessary.
Perform your own testing:
Oxidation Tech also builds Environmental Testing Chambers to our customer's specifications. If you prefer the ability to perform ozone exposure testing on-site view our ozone chambers HERE.
Should you have any questions about our ozone exposure testing services, please contact us.
Example of one of our ozone chambers in use: