Iron in cows drinking water can negatively affect milk quality.
A new study published in the Journal of Dairy Science has proven a link to poor milk quality due to elevated iron levels in drinking water on dairies. This new information gives more credence to the use of ozone for drinking water treatment on dairy farms.

While we have used ozone for iron removal in drinking water for dairies, along with many other water treatment applications, we did this for improved milk production, and higher water/feed intake reasons. This new study shows that even the milk produced from cows drinking water with elevated iron is of a lower quality due to iron in the drinking water.
Follow link below to see full paper:
http://www.journalofdairyscience.org/article/S0022-0302(16)30141-2/abstract
Milk protein composition and stability changes affected by iron in water sources
Abstract
Water makes up more than 80% of the total weight of milk. However, the influence of water chemistry on the milk proteome has not been extensively studied. The objective was to evaluate interaction of water-sourced iron (low, medium, and high levels) on milk proteome and implications on milk oxidative state and mineral content. Protein composition, oxidative stability, and mineral composition of milk were investigated under conditions of iron ingestion through bovine drinking water (infused) as well as direct iron addition to commercial milk in 2 studies. Four ruminally cannulated cows each received aqueous infusions (based on water consumption of 100 L) of 0, 2, 5, and 12.5 mg/L Fe2+ as ferrous lactate, resulting in doses of 0, 200, 500 or 1,250 mg of Fe/d, in a 4 × 4 Latin square design for a 14-d period. For comparison, ferrous sulfate solution was directly added into commercial retail milk at the same concentrations: control (0 mg of Fe/L), low (2 mg of Fe/L), medium (5 mg of Fe/L), and high (12.5 mg of Fe/L). Two-dimensional electrophoresis coupled with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–tandem time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF/TOF) high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry analysis was applied to characterize milk protein composition. Oxidative stability of milk was evaluated by the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) assay for malondialdehyde, and mineral content was measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. For milk from both abomasal infusion of ferrous lactate and direct addition of ferrous sulfate, an iron concentration as low as 2 mg of Fe/L was able to cause oxidative stress in dairy cattle and infused milk, respectively. Abomasal infusion affected both caseins and whey proteins in the milk, whereas direct addition mainly influenced caseins. Although abomasal iron infusion did not significantly affect oxidation state and mineral balance (except iron), it induced oxidized off-flavor and partial degradation of whey proteins. Direct iron addition to milk led to lipid oxidation during storage at 4°C. Oxidation level was positively associated with the concentration of added iron. Minerals (Mg, P, Na, K, Ca, Zn) in milk were not affected by the added iron in milk. This study indicated that a small amount of iron contamination in bovine drinking water at the farm or incidental iron addition from potable water sources causes oxidation, affects milk protein composition and stability, and affects final milk quality.
The Ozone Answer:
Ozone used with filtration can not only efficiently remove iron from drinking water, but also remove manganese, H2S, turbidity, and other taste/odor issues from water.
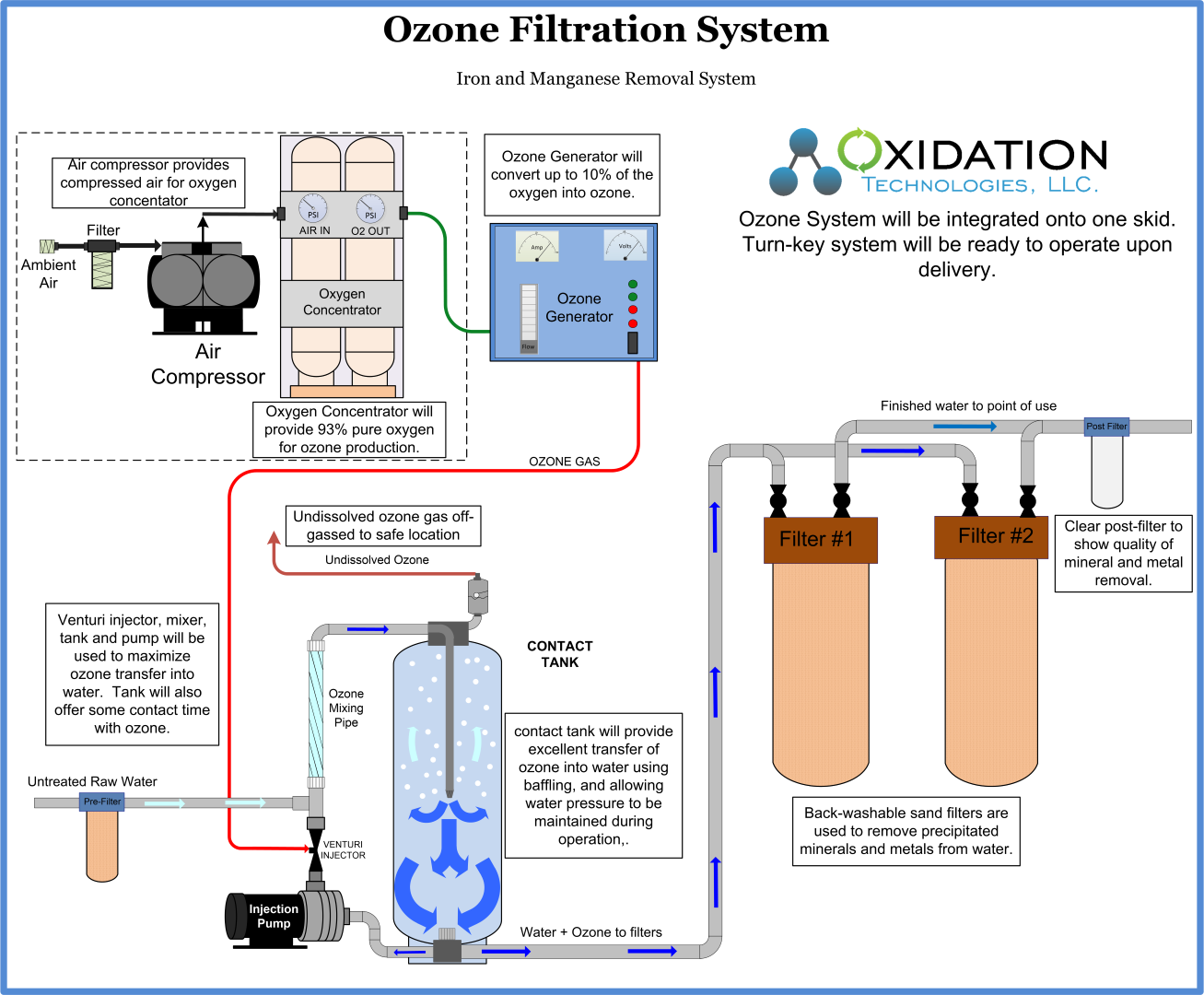
By using ozone for drinking water, better water disinfection can be realized without added by-products to the water. Also, increased dissolved oxygen levels will be present in water as ozone will break down into natural oxygen. Greater milk production has been realized from the use of ozone in dairy drinking water.
For help with your dairy, or any drinking water application give our engineers a call today. We would be glad to help.