BTEX removal with ozone
BTEX refers to mixtures of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and the three xylene isomers, all of which are aromatic hydrocarbons. Ozone has been proven effective at removing each of these hydrocarbons from water effectively. Each compound breaks down from ozone oxidation and leaves only CO2, H2O, and O2 as by-products.
BENZENE - Formula C6H6
Reaction with Ozone C6H6 + 11 O3 ---- > 6Co2 + 3 H2O + 11 O2
TOLUENE - Formula C6H5CH3.
Reaction with Ozone: C6H5CH3 .+ 18 O3 ----> 7 CO2 + 4 H2O + 18 O2
ETHYLBENZENE - Formula C8H10
Reaction with Ozone C8H10 + 7 O3 ----> 8 CO2 + 5 H2O
XYLENE - Formula C6H4C3)2
Reaction with Ozone C6H4(CH3)2 + 21 O3 ----> 8 CO2 + 5 H2O + 21 O2
BTEX removal with ozone has become widely used for in-situ remediation due to quicker clean-up times, and overall lower costs for remediation. Ozone has also been used to remove BTEX from water in pump-and-treat systems, and even in some drinking water systems where groundwater has been contaminated with high levels of BTEX.
Benzene:
Formula C6H6
Reaction with Ozone C6H6 + 11 O3 ---- > 6C02 + 3 H2O + 11 O2
Number of O3 molecules consumed per molecule of benzene = 5.5
3.38 grams of ozone are required to fully oxidize 1 gram of benzene.
Benzene molecular weight = 78.11
Ozone molecular weight = 48
1 gram benzene / 78.11 = 0.0128024581 * 48 * 5.5 moles of O3 = 3.38 grams of O3
Benzene (C6H6) is a clear, colorless and flammable liquid with a sweet petrol-like smell. Benzene is found in ambient air as a result of burning fuels, such as coal, petrol, and wood. Benzene is common in unleaded fuel, where it is added as a substitute for lead, allowing smoother running.
Benzene concentrations in fuel were once as high as 20%, but are now reduced to <1% in many countries, due to harmful health impacts. The World Health Organisation (WHO) and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classify benzene as a group one carcinogen. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of benzene causes leukemia and impacts red and white blood cells.
Less severe health impacts can occur at lower concentrations, causing headaches, nausea, drowsiness and even unconsciousness. The WHO has not set a standard for ambient benzene concentrations, stating that there is no safe level of exposure. Many countries use an annual average standard of 3.6 µg m-3.
In drinking water, the US EPA has set an enforceable regulation for benzene, called a maximum contaminant level (MCL), at 0.005 mg/L or 5 ppb.
In-Situ Remediation:
The chart shown below was generated based on data obtained from an in-situ remediation site. This chart shows the removal of both MTBE and BTEX on 2 separate wells.
Toluene:
Formula C6H5CH3.
Reaction with Ozone: C6H5CH3 .+ 18 O3 ----> 7 CO2 + 4 H2O + 18 O2
Number of O3 molecules consumed per molecule of toluene = 9
4.69 grams of ozone are required to fully oxidize 1 gram of Toluene.
Toluene molecular weight = 92.14
Ozone molecular weight = 48
1 gram toluene / 92.14 = 0.0108530497 * 48 * 9 moles of O3 = 4.69 grams of O3
Toluene (C7H6), also known as methylbenzene, is a colorless liquid, with a strong, solvent-like smell. Toluene is inexpensive and simple to produce and is widely used in industrial processes as a solvent. Significant amounts of toluene are used in industrial processes worldwide, with over US$20 billion generated from toluene sales in 2013.
In non-industrial uses, toluene can be found in petrol as an octane booster and in glues, solvents, and resins.
In drinking water, the US EPA has set an enforceable regulation for toluene, called a maximum contaminant level (MCL), at 1 mg/L or 1 ppm.
Ethylbenzene:
Formula C8H10
Reaction with Ozone C8H10 + 7 O3 ----> 8 CO2 + 5 H2O
Number of O3 molecules consumed per molecule of ethylbenzene = 7
3.16 grams of ozone are required to fully oxidize 1 gram of Ethylbenzene.
Ethylbenzene molecular weight = 106.167
Ozone molecular weight = 48
1 gram ethylbenzene / 106.167 = 0.0094191227 * 48 * 7 moles of O3 = 3.16 grams of O3
Ethylbenzene (C6H5CH2CH3), is a colorless liquid, with a petrol-like aroma. Ethylbenzene is widely used in industrial processes for the manufacture of styrene, which is then used for polystyrene manufacture. Ethylbenzene is also present as a solvent in inks, dyes and in petrol.
In drinking water, the US EPA has set an enforceable regulation for ethylbenzene, called a maximum contaminant level (MCL), at 0.7 mg/L or 700 ppb.
Xylene:
Formula C6H4(CH3)2
Reaction with Ozone C6H4(CH3)2 + 21 O3 ----> 8 CO2 + 5 H2O + 21 O2
Number of O3 molecules consumed per molecule of compound = 10.5
3.16 grams of ozone are required to fully oxidize 1 gram of Xylene.
Xylene molecular weight = 106.16
Ozone molecular weight = 48
1 gram xylene / 106.16 = 0.0094197438 * 48 * 10.5 moles of O3 = 4.75 grams of O3
Xylene (C8H10) is the term used to describe the three isomers of dimethyl benzene; m-xylene, p-xylene, and o-xylene. Usually, concentrations of each are added together as total xylenes. Xylene is refined from crude oil and is a clear, greasy liquid.
Xylene is widely used in the production of plastic bottles and polyester clothing and as a solvent with a range of applications from circuit board cleaning to thinning paints and varnishes.
In drinking water, the US EPA has set an enforceable regulation for xylenes, called a maximum contaminant level (MCL), at 10 mg/L or 10 ppm.
Our Results:
We have used ozone for BTEX removal for both in-situ and pump-and-treat applications with great success. BTEX oxidation is completed quickly and completely with ozone.
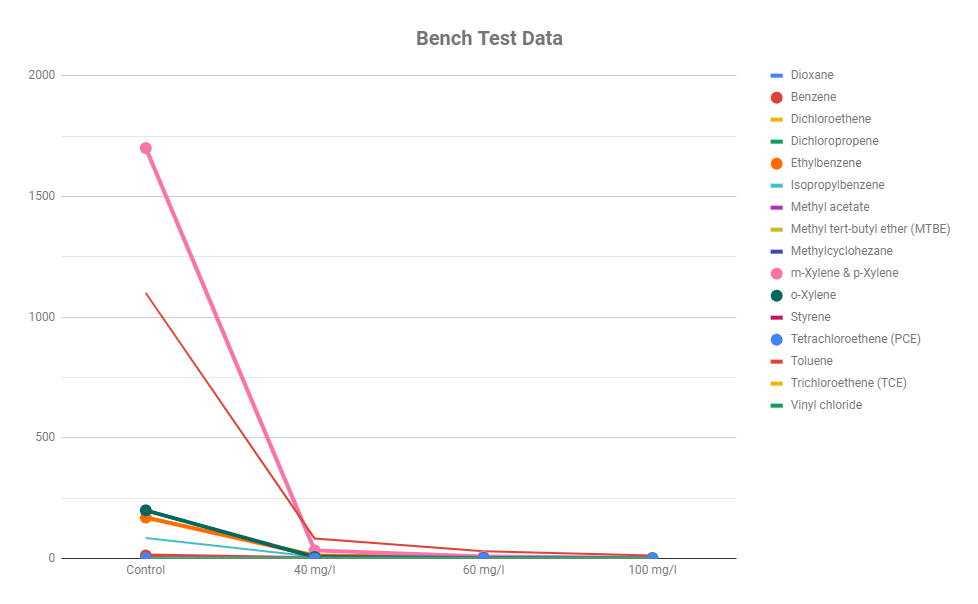 |
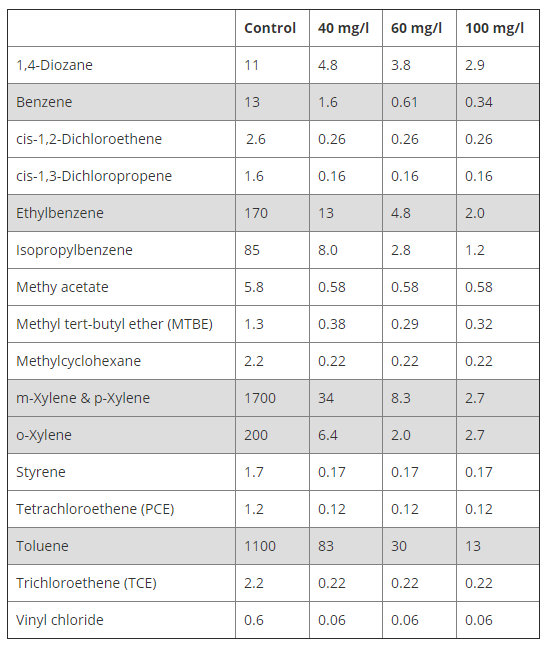 |
These results are from a bench-test we performed to evaluate ozone demand for a pump and treat system we later implemented.
Click HERE for additional site data using ozone for in-situ remediation.
In-Situ Remediation:
For in-situ chemical oxidation applications, we offer a variety of systems and options. Complete turn-key trailers are commonly used. We also offer modular systems to allow the end-user to install the system in an existing enclosure on-site. This may be helpful for a retrofit, or to lower costs by using existing infrastructure.
In these applications, ozone is produced as a gas from oxygen. This ozone is pushed through tubing to the bottom of a well and diffused at the bottom of the well in the water table. Ozone will dissolve into water in an area around each well treated breaking down the BTEX in that area. The ozone system will normally treat multiple wells on a single site by switching between wells periodically. As ozone has a half-life and will continue to break-down BTEX after sparging is shut-off there is added benefit to treating 15 wells with a system that has the capability of sparging to only 5 wells at a time.
Pilot systems are also available for In-situ remediation for short-term tests. We currently have ozone trailers available for these applications:
 Trailer mounted ozone systems Trailer mounted ozone systems |
 Modular ozone systems Modular ozone systems |
 Cabinet mounted ozone systems Cabinet mounted ozone systems |
All new ozone systems for remediation applications
Pilot systems currently available
Pump and Treat:
This refers to any system that will treat water in a flow or process. We offer ozone injection systems that are typically skid mounted to be installed in existing infrastructure. A standard ozone water system will consist of an ozone generator that generates ozone from oxygen, an ozone injection pump and venturi to dissolve ozone gas efficiently into water and an ozone mixing tank to allow ozone gas time to dissolve into water, while off-gassing excess ozone from the process.
Based on the level of BTEX in water and other contaminants that require oxidation we can help develop the right pump and treat system for your application. Exact ozone dosage rate, contact time, and technology used should be based upon the levels of BTEX in water and the other potential contaminants found in the water.
Pilot test systems are available, we can also provide bench-scale testing services to determine if ozone is a viable option for your water.
Pilot test system for rent currently available
Technical Documents:
Below is a series of papers and documents outlining practical and laboratory success in the elimination of BTEX from water using ozone, or ozone AOP processes.



 BTEX Remediation under Challenging Site Conditions using In-Situ Ozone Injection and Soil Vapor Extraction Technologies: A Case Study
BTEX Remediation under Challenging Site Conditions using In-Situ Ozone Injection and Soil Vapor Extraction Technologies: A Case Study













